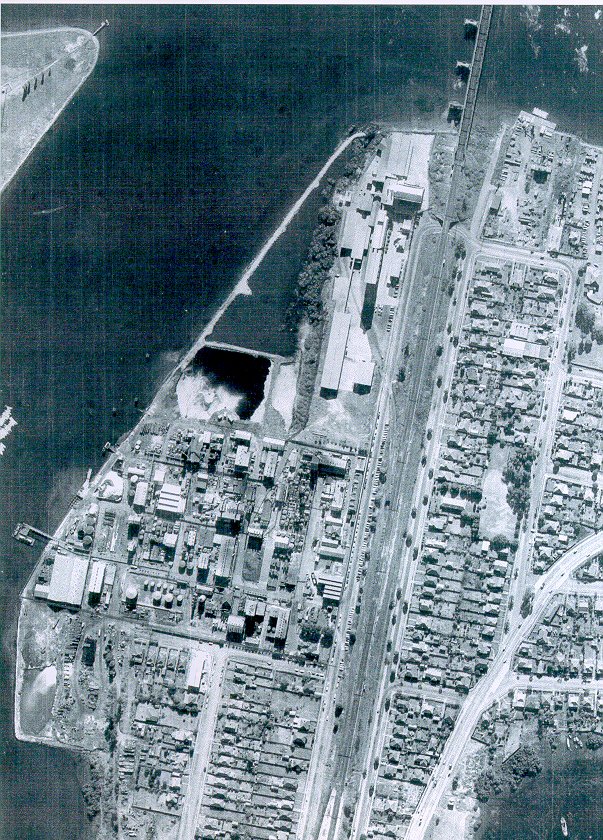
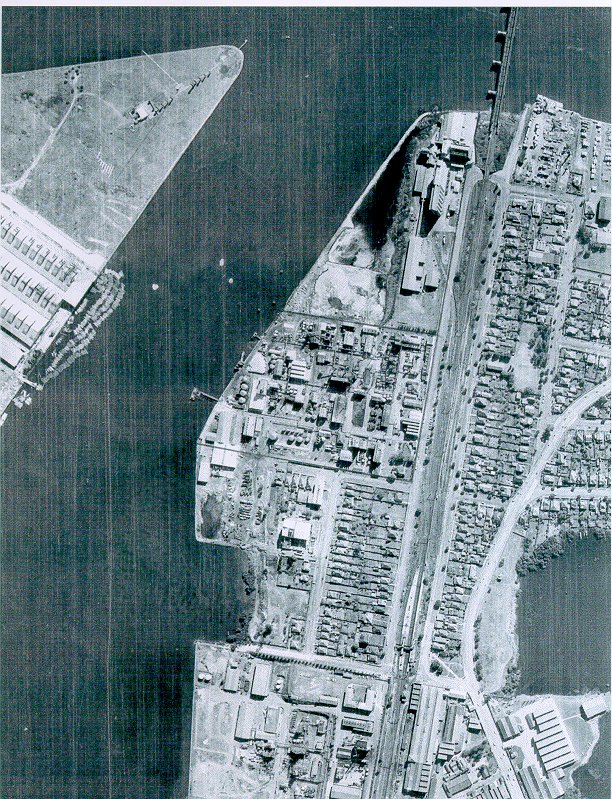
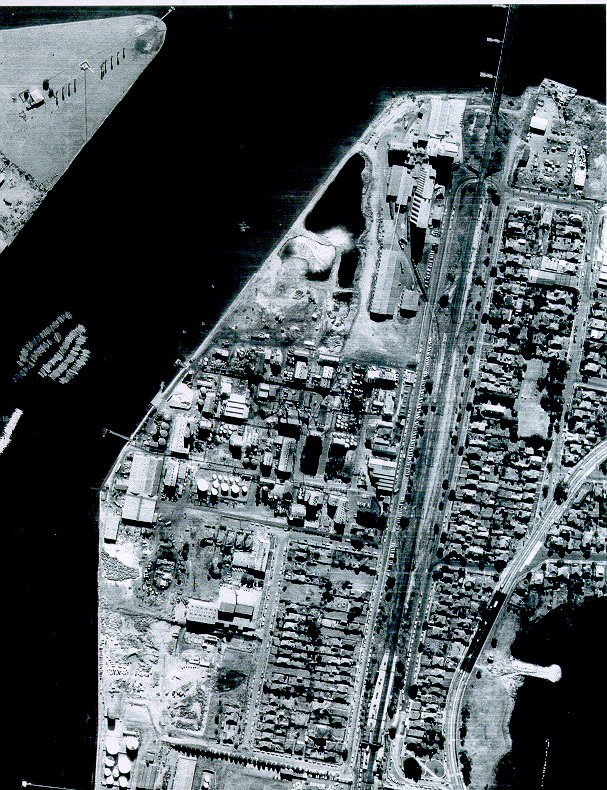
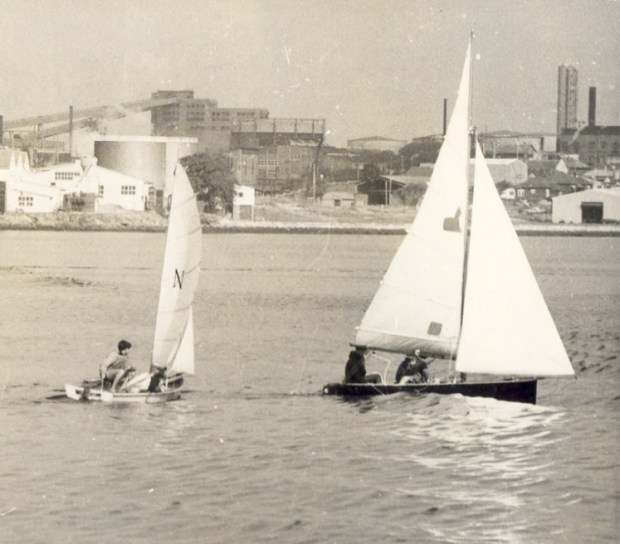
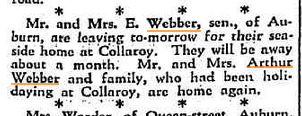Past/Lives Flashback #1: Union Carbide – Rhodes, NSW
Original article: Timbrol Chemicals/Union Carbide/Residential – Rhodes, NSW
Yes, the time has finally come. The most popular entry on Past/Lives over the last year (and a bit, by this point) by far was the tragic tale of Rhodes and that most toxic tenant, Union Carbide. Rhodes’ decimation at the hands of industrial abuse throughout the 20th century and subsequent resurrection as a residential paradise in the 21st is a long story, and one with repercussions for the whole of Sydney even today. Grab a coffee (although Rhodes residents, maybe don’t use tap water) and get comfortable…we’ll be going back over the whole thing.
THEN
Rhodes Hall, near Leeds, was about as far from the eastern shore of the picturesque Homebush Bay as Thomas Walker could imagine. A commissary, Walker had arrived at Port Jackson in 1818, and the following year bought an allotment of land from Frederick Meredith, another early settler. Walker built a house on his bank of the Parramatta River, naming it Rhodes after his grandmother’s estate back in the motherland because even hardened and worldly mercenaries still have soft spots for their grannies. So soft, in fact, that in 1832, Walker moved to Tasmania where he built another estate…also named Rhodes. She must have spoiled that kid rotten.
The Walker family relinquished their control over the Rhodes estate in 1919, when they sold up to the John Darling Flour Mill. By this point, Rhodes was no stranger to industry. Eight years earlier, G & C Hoskins had cleared much of the area’s forests to erect a cast iron foundry, and once this had happened, everyone got on board. There was little resistance to this kind of heavy industrialisation, especially in a suburb like Rhodes, which was easily accessible by rail and water.

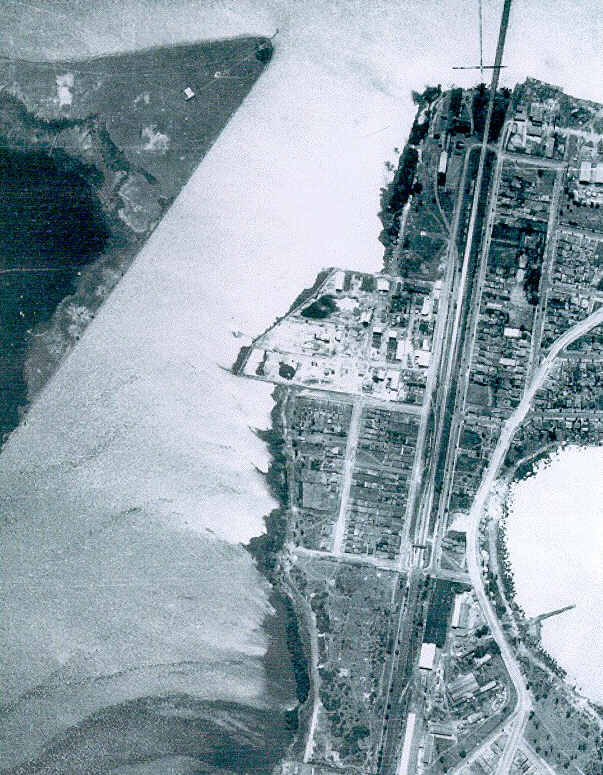
Kind of looks like the silhouette of a guy with a ponytail, doesn’t it? Image courtesy City of Canada Bay.
At this point in time, Rhodes and the neighbouring Homebush were the outer limits, truly the Western Suburbs, with only Parramatta and the Blue Mountains more forbidding. Sydneysiders were keen to get the blossoming industrial sector as far away from their own backyards as possible (understandably), and Rhodes, bordered by the new abattoir and the Parramatta River, was out of sight, out of mind.
Flour mills and cast iron foundries weren’t exactly environmentally friendly (a phrase not yet in use in 1928), but the true damage to Rhodes didn’t begin until the arrival of Timbrol Ltd in 1928. Timbrol had been established in 1925 by three Sydney University researchers keen to manufacture their own brand of timber preservative, so at least it was all for a good cause.
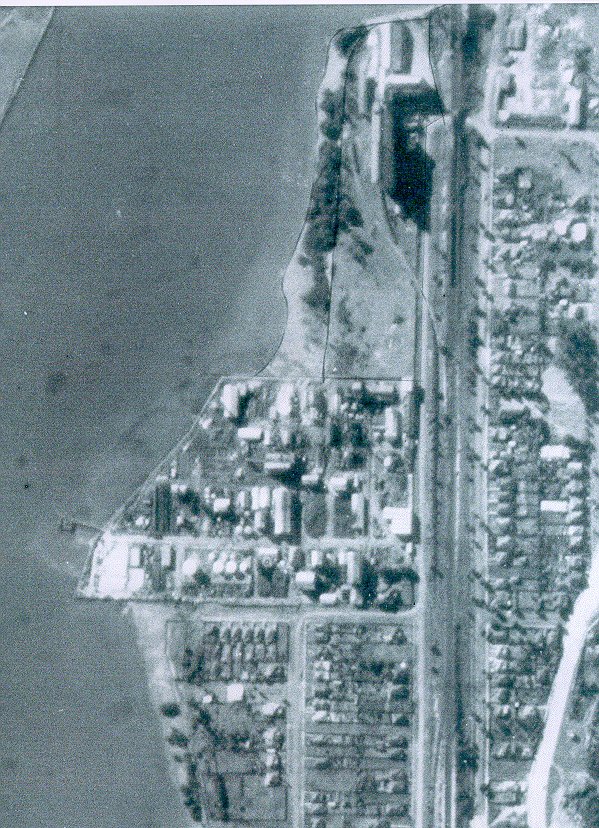
In 1933, Timbrol had a breakthrough! It was able to produce the first Australian made xanthates, which is used in the mining sector for extracting particular kinds of ores. With the advent of the Second World War, xanthate exports boomed, and expansion of the Timbrol site was required. But where to go? Sandwiched between the train line and the foreshore, and with John Darling to the north and CSR (another booming wartime chemical company) to the south, Timbrol was apparently out of options.
Just joking. Of course there was an option – the only option: reclaim land from Homebush Bay by filling in the river with contaminated by-products and building over it. Out of sight, out of mind.
The post-war housing boom brought about various new challenges in the domestic domain, most of which could be easily solved with chemicals. Thus, demand for chlorine, herbicides and insecticides, particularly DDT, skyrocketed, and Timbrol was right there to capitalise. And by right there, I mean jutting out over Homebush Bay on new, hastily constructed ground.
Spurring the chemical company’s efforts on even further were their competitors CSR, ICI and Monsanto, most of whom were a stone’s throw away from the Timbrol site. The close proximity of these companies meant that the output of potentially dangerous by-product seemed minimised in the eyes of the era’s governments; it was better for all the companies to be dumping together rather than dumping apart at wider intervals. This also meant that the neighbouring sites could ‘borrow’ Timbrol’s approach to expansion – good news for Homebush Bay.
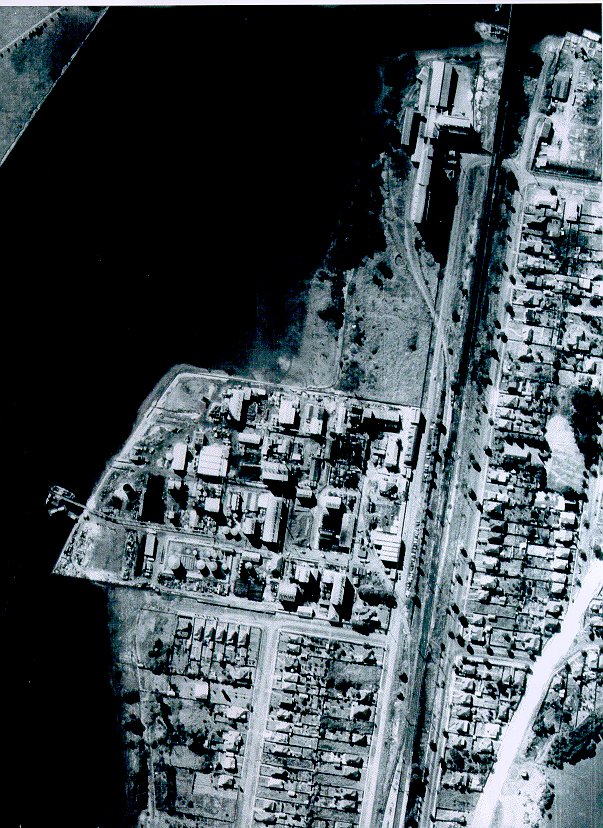
Timbrol’s success had attracted another element: the American chemical giant Union Carbide, which saw Timbrol as a great place to start an Australian subsidiary. Union Carbide dated back to 1898, and had built its wealth through aluminium production and its zinc chloride battery arm – both of which seem like the perfect thing to manufacture on the bank of a serene body of water.
At this point I’d like to pose a question: when did it ever seem like a good idea to produce chemicals like herbicides, zinc chloride and xanthates beside a healthy bay full of wildlife? Who signed off on this? How were the guys in charge of these companies able to look at this beautiful place and think “Hmm, needs more poison.”? I’m aware that without these chemicals we wouldn’t be able to live the way we do today, but some of these decisions were bordering on just straight up evil.
The arrival of Union Carbide frightened Timbrol’s competitors. The might of the American parent company meant near-unlimited resources, so local campaigns were stepped up.
CSR and even old John Darling began to encroach upon the bay, re-sculpting the landscape as they saw fit.
The initial success of Union Carbide Australia didn’t go unnoticed overseas, either. Associated British Foods bought John Darling’s Flour Mill for its Australian subsidiary Allied Mills in 1960, rebranding it Allied Feeds. Most of the product manufactured at the Allied Feeds site would end up in the stomachs of livestock sent to Homebush Abattoir, where said stomachs would then be carved up to be fed back to the populace. And for that, you need MORE ROOM.
But back to Union Carbide. The early 1960s weren’t kind to UC. Competitors and waning demand had teamed up to diminish the brand, but that didn’t stop the near endless flow of poisons into the bay. By now, nearly all of Union Carbide’s output produced an unfortunate and extremely unpleasant by-product: dioxins. Highly toxic and capable of, at the very least, causing cancer and damaging reproductive and immune systems, dioxins are usually exposed to humans via food particularly meat and fish. What a great idea then to produce extremely unsafe levels of dioxins right beside a manufacturer of animal feed. What a great idea to produce that animal feed on top of land infused with dioxins. What a great idea to expel those unwanted dioxins into Homebush Bay, a waterway directly linked to Sydney Harbour and full of fish.
Let’s take a moment to hear from the World Health Organisation about dioxins:
Short-term exposure of humans to high levels of dioxins may result in skin lesions, such as chloracne and patchy darkening of the skin, and altered liver function. Long-term exposure is linked to impairment of the immune system, the developing nervous system, the endocrine system and reproductive functions. Chronic exposure of animals to dioxins has resulted in several types of cancer. Due to the omnipresence of dioxins, all people have background exposure and a certain level of dioxins in the body, leading to the so-called body burden. Current normal background exposure is not expected to affect human health on average. However, due to the high toxic potential of this class of compounds, efforts need to be undertaken to reduce current background exposure.
So…don’t do what Union Carbide did next, then?
The fortunes of Union Carbide Australia were reversed by the Vietnam War. See, Vietnam has a lot of jungles, and those pesky Vietcong kept hiding in those jungles, so what better way to flush them out than by removing their hiding spot? Union Carbide was contracted by the US military to produce Agent Orange, a dioxide-heavy defoliant. Even when it was discovered that Agent Orange’s components contained a particularly toxic strain of dioxin, it continued to be sprayed indiscriminately throughout the war, during which dioxins continued to be dumped into Homebush Bay.
In the midst of all this, Union Carbide research scientist Douglas Lyons Ford invented Glad Wrap at the Rhodes plant. It was introduced to the Australian market in 1966, the first such product in the country. Well, that kind of balances out that other thing, doesn’t it?
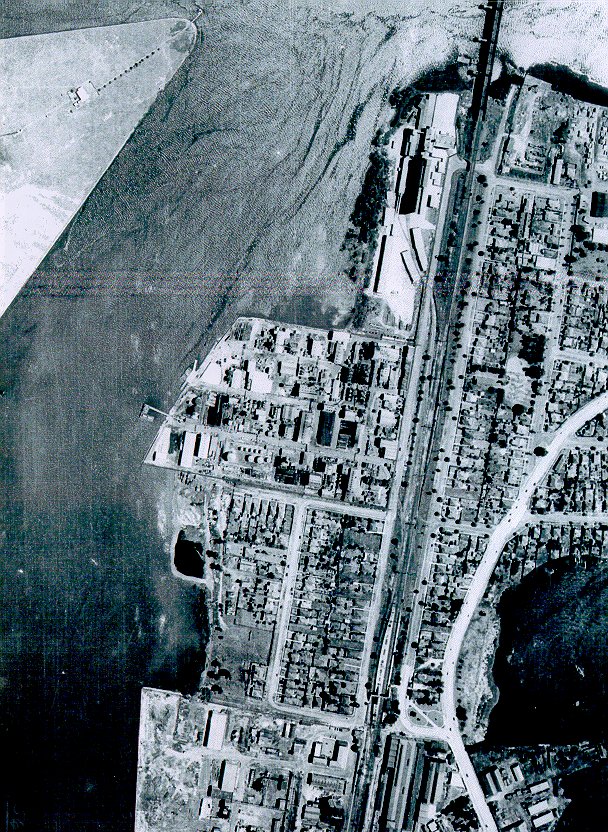
By the 70s, environmental action against companies like these was stepping up, and the population of Sydney had exploded westward. Rhodes’ train line was now a sharp divider between the industrial zone and a booming residential sector.
Further north and across the river, Meadowbank and Ryde were both beginning to cast aside their industrial legacies and welcoming more and more families, while to the south, the Homebush Abattoir was winding down operations. Forward-thinking residential developers were eyeing these areas with great interest, and keeping government wheels greased to ensure their availability in the future. In typical lightning fast Sydney reaction time, this movement was accommodated in the mid-80s by the construction of Homebush Bay Drive, a highway that bypassed the nearby suburb of Concord and tracked through Rhodes’ industrial zone. Out of sight, out of mind.
By the early 1980s, Rhodes was known throughout the land for its toxicity and odour above all else.
Its rich legacy of achievements in the field of chemistry long forgotten, Union Carbide was looking increasingly sick and tired; a relic of another age. But one major incident in 1984 made it look downright villainous.
In December of that year, an explosion at the Union Carbide plant in Bhopal, India exposed half a million people to toxic gases, killing thousands. PR disaster for UC, and the final straw for the parent company. Most of its international subsidiaries were wound up in the years following Bhopal, including the Rhodes plant, which ceased operations in 1985. Allowed to leave without any kind of cleanup effort, Union Carbide left behind a toxic legacy that remains detrimental to Sydney today.
The NSW Government and the Australian Olympic Committee had hoped to transform Rhodes into an Olympic athlete village by the 2000 Sydney games, but they had underestimated just how poisoned the land was.
Government remediation efforts tried in vain between 1988 and 1993 to heal the land, but it wasn’t until 2005, long after the end of the Olympics, that private enterprise intervene with the necessary money and technology to properly clean the land. Why this sudden burst of effective effort so long after the fact?
NOW
Today, if you turn off Homebush Bay Drive at the IKEA, you’ll descend into valleys of glass and steel. Rhodes’ rebirth as a gauntlet of residential and commercial towers, a process which began in 2005, is nearly complete. Sensing an opportunity to make money, Mirvac and other developers pounced on the toxic wasteland at the end of the 90s, saving it from a future of causing people to hold their breath as they drove past.
With a steady flow of money and the promise of even more at the end of the remediation rainbow, Thiess and the NSW Government got to work turning the poisonous dirt into the foundations of the futuristic castles that line the foreshore today.
But while the reclaimed land has been mostly made harmless, the bay has not. In fact, the NSW Department of Health has prohibited fishing west of Sydney Harbour Bridge due to an abundance of dioxins. And swimming? Forget it.
The remediation efforts have been effective in more ways than one. I don’t think that Mirvac and friends really cared about anything other than making the land safe enough to pass re-zoning as residential, but despite this, wetland wildlife has begun to return to the bay. Studies on the sea life are ongoing with hopes that one day the bay will once again be safe, but I don’t think we’ll see it in our lifetime. To my infant readers: this means you too.
To the developers’ credit, the project seems to have largely been a great success. There’s the popular shopping centre, complete with cinema and IKEA (a huge coup in its day, since superseded by Tempe), and Liberty Grove to the east. Care has been taken to eradicate most traces of the industrial nightmare of the past. The new units look good enough to stop you from wondering why the grass is always yellow, and they’re certainly filling up fast. And yet…
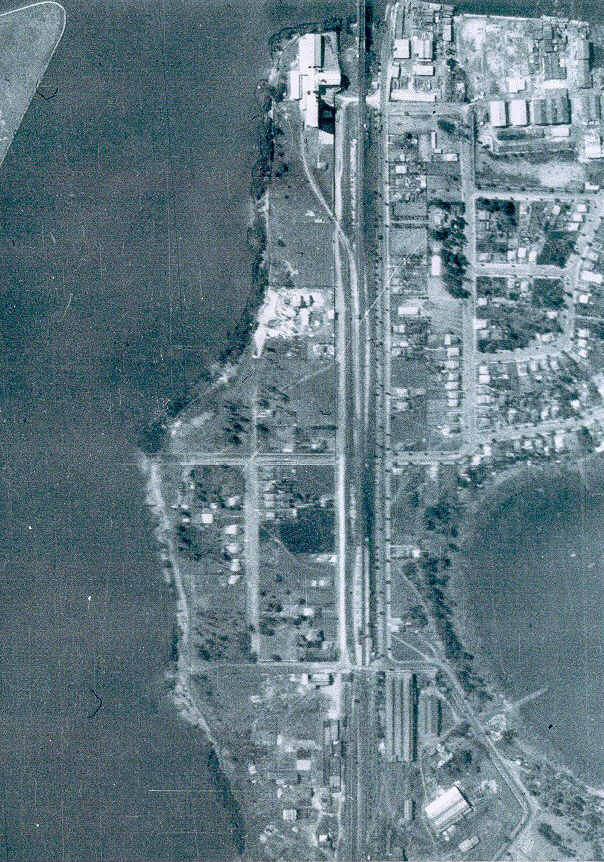
If you plant a seed in bad soil, it won’t grow very well. Case in point: this is the unit tower being constructed directly upon the former Union Carbide site. Every other tower in Rhodes is either completed or is only weeks away, but not Union Carbide. In fact, the entire site seems to have been plagued with construction delays or other issues. Sure, this stage of the Rhodes project started later than the others, but that too is down to the sheer toxicity of the Union Carbide land.
At the rear, things look even worse. Piles of dirt sit around, uglifying the scenery. Cranes hover above the unfinished structure like buzzards.
On the corner of Shoreline and Timbrol, construction equipment is a mainstay. It’s as if they just can’t make this one happen, despite their money and intentions.
Tower number two hasn’t even started yet, acting as a base of operations for the workers completing tower number one. In 1997, Greenpeace discovered 36 sealed drums of toxic waste underneath the Union Carbide site, so there’s no telling what these guys are digging up as they go. Does your underground carpark glow in the dark?
Down at the Union Carbide foreshore, an even eerier sight: completed units, completely empty.
These seem to be ready to go, but either due to environmental concerns or the noise of construction, residents aren’t allowed to move in yet. I’d be leaning toward the former reason, seeing as plenty of other people here have to put up with the noise.
The Rhodes experiment has proven to be an environmental triumph, arguably even greater than Sydney Olympic Park, but it’s an even greater financial triumph. The corporations behind the remediation weren’t doing this for the sake of the environment or because they felt like doing something nice, they were doing it for the exact same reason the land was stained in the first place. Rhodes may have gotten the second chance Bhopal never did, but they’re equally valid testaments to that reason.
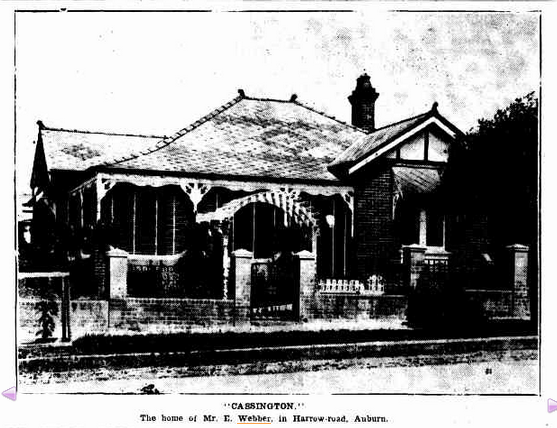
The Auburn Emporium – Auburn, NSW
Let’s take another trip to that seemingly bottomless well of source material, Parramatta Road. If this Australian Women’s Weekly logo looks ancient to you, that’s because it is. In fact, I’d say there’s a good chance the magazine itself sported this logo the last time it was on sale at this location, which was most recently known as Danny’s Newsagency. But what’s happened to the sign there?
Oh, well this changes everything. Before Danny moved in, the newsagency was Brown’s domain. Perhaps the AWW sign belonged to Brown in the first place. Case closed, unless the awning offers us any more clues…
 No. It was Brown’s Newsagency, then Danny’s, and now it’s a freight company called BLM, which is apparently just too busy to take down some old, misleading signs. Mission accomplished, what a great story, we can all go home. Was it good for you too? Seriously, why can’t these shops just present a decent front? If BLM wanted more business, why wouldn’t they dust themselves off a bit (unless they don’t want more business ON PURPOSE)? Does the rest of this row of shops have the same issue?
No. It was Brown’s Newsagency, then Danny’s, and now it’s a freight company called BLM, which is apparently just too busy to take down some old, misleading signs. Mission accomplished, what a great story, we can all go home. Was it good for you too? Seriously, why can’t these shops just present a decent front? If BLM wanted more business, why wouldn’t they dust themselves off a bit (unless they don’t want more business ON PURPOSE)? Does the rest of this row of shops have the same issue?
On the east corner we’ve got Blossoms wholesalers of health, beauty and ugg. Great combo. Looks like they ran out of yellow paint before they could disguise the fact the place used to sell:
..’beding’, among other things. Great. What’s that up there?
You can’t have freezers without fridges. Oh look, the building was finished in 1912. I bet they weren’t this lazy or negligent back then. Next…
 The next door down offers no such insights – it’s a boring restaurant. Beside that, it’s this accountant. And a pretty busy one right now I’m sure, given what time of the year it is. Yawn…I’d imagine this place wasn’t so pedestrian in 1912, a time when Parramatta Road wasn’t a huge embarrassment to the city and a great place to park your car on weekends. It would have had a purpose, it would have been the product of some dude’s life’s work. It would have stood out from the crowd and meant something rather than just taken up space with its ugliness.
The next door down offers no such insights – it’s a boring restaurant. Beside that, it’s this accountant. And a pretty busy one right now I’m sure, given what time of the year it is. Yawn…I’d imagine this place wasn’t so pedestrian in 1912, a time when Parramatta Road wasn’t a huge embarrassment to the city and a great place to park your car on weekends. It would have had a purpose, it would have been the product of some dude’s life’s work. It would have stood out from the crowd and meant something rather than just taken up space with its ugliness.
Yeah, I’d like to think this was something really special…back in the day…
Mr. Webber had sold his other business at nearby Rookwood, presumably the one on which he had built his name, because he had such faith in this place. Wow. “The windows are a picture.” Wow! They sold pianos and had the Auburn Brass Band on site to celebrate the opening. It’s hard to believe that such an event could once have gone on at this place we’ve seen today, but there you go.
Don’t let anyone tell you department stores aren’t a cut-throat (or cut-head, in this case) industry, just like I won’t let anyone tell me that Wylie’s departure from Webber’s empire and Arthur Webber’s injury are just a coincidence. In fact, let’s concentrate on Wylie’s little advertisement for a moment. First, he’s taken it out in the accidents section of the paper, which doesn’t bode well. Second, he’s done it directly below an account of his former employer’s misfortune. Third, he’s included the snide ‘up-to-date Store’ dig, as well as imploring thrifty shoppers to ‘compare his prices’ (to whom, I wonder?)…and yet the very next line tells you there’s one one price to compare. In case you’re interested, his address is a Westpac bank today, which means this paragraph is his legacy. Suck it down, Wylie.
Gee, the Webbers seem a little…accident-prone, don’t they? In 1921 young Ernest Webber (son of Arthur) cut his finger. And it made the paper. Slow news year, perhaps?
So successful was the Webber store that a Mrs. Middleton took the fight to Merrylands. I wonder how it turned out?
Ernest E. Webber (who I’m assuming isn’t the seven-year-old with a bandaid on his finger) copped a heavy fine of four pounds for not paying two of his employees the minimum wage. No wonder Wylie left. Shoulda just paid ’em, Ernie.
Just don’t expect minimum wage. Hey, what a deal there at the top: a set of teeth from one guinea. Yuck.
The Webbers, still in PR crisis mode, provide the furnishings to a local recital. We haven’t forgotten about the third world wages, Ern.
And neither has Desire La Court (what a name). Read that thrilling tale of escape in the third paragraph, and tell me it wouldn’t make a great white-knuckle thriller starring Channing Tatum.
Here’s Webber’s castle, paid for by the unpaid wages of his workers.
I can’t decide whether my favourite part of this story is the thief begging Webber not to call the cops and then offering to drive Webber to the police station, or him playing the ‘my wife and kids’ card for sympathy and later denying having done so. It’s just a quilt, Webber. Even if he did nick it, let him have it. The Depression’s coming.
And now they know: don’t throw a lit cigarette onto piles of paper.
Good thing they advertised this, now all the thieves out there with a copy of the 1927 paper and a map will know his house is empty.
Young Ernest Webber, last seen blubbering like a baby over a cut finger, has turned 21. Lock up your daughters! Nice cheapskate present, Dad – an autographed key. “My signature will be worth a lot of money in a few years, son…”
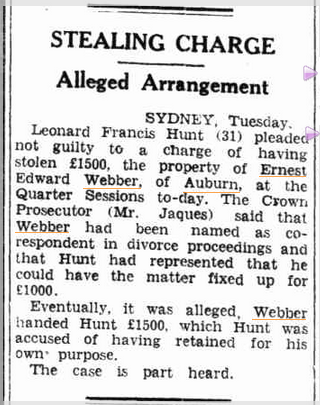
Do you think Mark Foy was this plagued by thievery?
This plagued? This seems just a little suss, don’t you think?
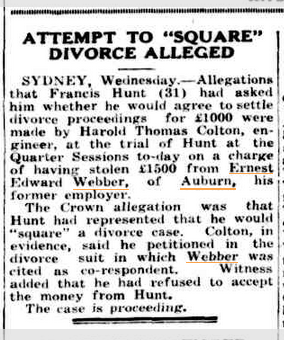
The plot thickens. I like the use of quotation marks around “square”, as if to square this divorce meant some drastic action.
And finally the truth comes out! Picture the headlines: “Webber of Deceit”. I wonder if Webber’s trip to Jervis Bay was advertised in the paper? Maybe all those other times Webber was thieved from was the result of some cuckolding. I can only imagine how his wife must have felt…
Oh.
From philandery to philanthropy. Wisely replacing the adulterous E. Webber as media spokesperson, Arthur Webber sets off on his quest to repair the Webber reputation, 150 shoppers at a time. I’m guessing they had a sign, “Toilet and air-raid shelter for customers only.”
With the war over, the Webbers put some distance between the scandals and tragedies of the past by backing the Auburn ‘Popular Girl’ Competition. Really rolls off the tongue, doesn’t it? You’re pretty much asking for trouble inviting someone named ‘Mrs. Crooks’ to your fancy ball, especially given your history, Webbers.
Sadly, this grand event is where the Webber story comes to an end. The trail went cold, and nothing more hit the papers. But despite the abrupt and mysterious ending it kind of feels like we were right there with them…almost like we were one of them. Do we need to know what happens next? Do we need the sad details of the day the Webbers signed their pride and joy over to Brown of Brown’s Newsagency? Of the day one of the shops was demolished to make room for Gypsy Leather, ruining the established style? Probably not. The best years are behind us at this point, and we’ve only the advent of Danny’s Newsagency to look forward to. We can use our imaginations to fill in the blanks.
Plus it’s been an adventure. We’ve laughed, we’ve cried, we’ve been scandalised and burglarised, but above all, we’ll never look at this innocuous little row of shops with the same eyes again. Right? Here it is again, just to be sure:
Devonshire Street Cemetery/Central Station – Sydney, NSW
“I once walked through the burial grounds on the Surry Hills, in the commencement of Spring, just as the flowers were beginning to bloom forth in all their beauty…”
Bridget Flood was in the same situation too many of us have found ourselves in all too often: stranded at Sydney’s Central train station, hopelessly late. The big difference is that she was waiting there for over 60 years.
As we’ve previously learned, 1820 was a good year to die in Sydney. Rather than ending up beneath the public piss-pot that was once the colony’s first burial ground, you could find yourself in a brand new plot freshly dug at the just-consecrated Devonshire Street Cemetery.
Chosen for its abundance of space and central (heh) location, the area bordered by Elizabeth and Devonshire streets was chosen to replace the Old Burial Ground as Sydney’s premier final resting place. Quartermaster Hugh McDonald, 40, was the first lucky stiff to be buried there following his death in 1819. Long waiting lists…so Sydney so chic.
“It was early in the morning when I commenced rambling amongst the tombs, the dew had not yet been dissipated by the genial rays of the invigorating luminary, and the cool fragrance of the atmosphere had not yet given way to the noon-day heat…”
Bridget Flood died in October 1836 at the age of 49 and, like virtually all deaths in Sydney at the time, was interred at the Devonshire Street site. Quoth her headstone:
“Pain was my potion
Physic was my food
Groans were my devotion
Drugs did me no good
Christ was my physician
Knew what way was best
To ease me of my pain
He took my soul to rest.”
They don’t write ’em like that anymore. And rest she did, as did all those buried at Devonshire Street Cemetery well past its 1867 closure.
Although steadily employed by the city’s dead between 1820 and 1866, the nail in the coffin (heh heh) for the cemetery was the latter year’s introduction of the Sydney Burial Grounds Act (NSW), which prohibited burials “within the city of Sydney from 1 January 1867, with the exception that persons with exclusive rights of burial at that date could still be buried on application to the Colonial Secretary who needed to be satisfied that ‘the exercise of such right will not be injurious to health’“. Phew. Just tie some rocks to me and throw me in the harbour!
You’d think this act would be in anticipation of some kind of grand plan for the burial ground, but no. With the exception of infrequent additions to family plots as outlined by the overly wordy act (and even these ceased in 1888), Devonshire Street was largely ignored by the growing city while new sites like Waverley Cemetery and the Rookwood Necropolis served the public’s burial needs.

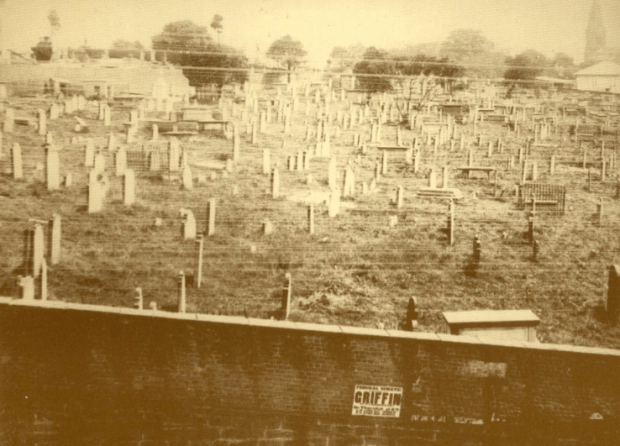
Prince Alfred Park’s Exhibition Building looms large. Devonshire Street Cemetery, 1901. Image courtesy Royal Australian Historical Society.
By 1900, its advanced state of neglect and decay reflected its residents and disturbed the public:
…although it wasn’t all bad:
“In short, it was exactly such an hour as an imaginative or sensitive being would delight to rove about, and lose himself in the regions of fancy…”
It wasn’t long before some of the more opportunistic voices began to speak out about the the site’s real estate value:
And as early as 1888 there were rumblings about how best to use the land:
It made sense, given that Central Station’s predecessor, ‘Sydney Station’, lay opposite the cemetery along Devonshire Street.
Since 1884, Sydney’s existing rail network had been under the stress of increasing traffic and a limited reach (sounds familiar, doesn’t it?). Sydney Station was constantly receiving upgrades and additional platforms, culminating in a messy setup of 13 train platforms and numerous tram sheds (sounds familiar, doesn’t it?). The city’s railway commissioners initially struggled to decide upon a plan for the future which would provide Sydney with a central hub expansive enough to extend the rail network to the suburbs (sounds- never mind).
An 1897 royal commission proposed the resumption of Hyde Park for use as the central terminal and, to counter the public outrage over the loss of parkland, the Devonshire Street Cemetery would be converted into a park. For a time this plan seemed to be a go until the unexpected death of Railway Commissioner E M G Eddy (of Eddy Avenue fame) that same year. This forced a literal return to the drawing board, where it was decided that it was probably easier to resume just one giant park instead of two. Nice thinking, guys.
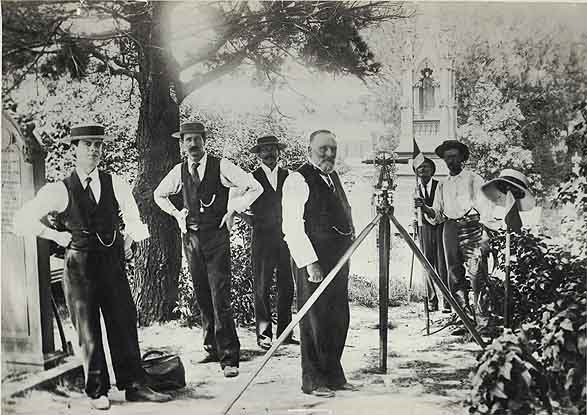
In January 1901, the Department of Public Works served notice that anyone with relatives buried at Devonshire Street were to front up and make known their desire to have the remains reinterred at other cemeteries by train, with the cost to be borne by the NSW Government. These days, they’d just tell you to bring a shovel.
Unfortunately, these relatives were given a strict time limit of two months to act, and by the end of that time, only 8,460 bodies had been claimed (not among these was Eddy, who had been buried at Waverley following his death). This left 30,000 remains unclaimed, most of which were transferred to other cemeteries anyway, but due to the rushed nature of construction and given they did such a bang-up job the last time, it’s safe to say there are more than a few commuters at Central waiting for a train that will never come.
With that many bodies to exhume, you can imagine just how many creepy stories must have come out of the venture. Here’s just one:
The reason for the rush was that Melbourne had started work on their Central equivalent, Flinders Street Station, that same year. Sydney was determined to get the drop on Melbourne this time, as Flinders predecessor ‘Melbourne Terminus’ had been Australia’s first city railway station back in 1854, pipping Sydney by a year. The Devonshire Cemetery site had been completely cleared by 1902, and stage one of Central’s construction, which aimed to have the station operational, was completed in 1906. On opening day, the new station featured…13 platforms. Despite being twice the size of its predecessor, this was no improvement, and did nothing to alleviate Sydney’s transport woes (but then again, what ever does?).
“I directed my footsteps to a cluster of tombs on an eminence, which was thickly covered with green and blooming geraniums…”
But the unexpected fruit of the Department of Public Works’ labour was the emergence of commercial activity in the areas surrounding the new station. Its proximity to the city made department store shopping for those out in the sticks a treat, with Grace Bros., Marcus Clark, Anthony Hordern, Bon Marche and Mark Foy all within walking distance of Central by 1908. The Tivoli and Capitol theatres became entertainment meccas for those starved of entertainment in the ‘burbs.

Anthony Hordern awaits new business during Central’s construction, April 1903. Image courtesy ARHS Rail Resource Centre.
The station itself was hardly the thing of beauty its early designs had suggested, with the rushed development cycle omitting many intended features – least of all Central’s iconic clock tower, which wasn’t completed until 1924.
The construction wasn’t just focused on making sure the station would be operational before Flinders Street, though; there was particular care taken to ensure no trace of the Devonshire Street Cemetery remained, going so far as to completely eradicate Devonshire Street west of its intersection with Elizabeth. Other structures that once stood on the land now occupied by Central and its surrounds – the Belmore Police Barracks, the Benevolent Asylum, the womens refuge – have similarly been lost to time.
“I at first almost forgot the ravages of the grave in contemplating the enchanting appearance of the place.” – James Martin, 1838.
Today, nothing remains to remind commuters of the morbid nature of Central’s past. The cemetery itself was largely situated underneath today’s platforms:
Devonshire Street Tunnel, once Devonshire Street, runs directly underneath the path once carved between the cemetery and Sydney Station, depositing Surry Hills pedestrians into Railway Square amid el-cheapo bargain shops, youth hostels and fast food joints.
Also in Railway Square is a series of plaques designed to inform passers-by on the history of Central Station and railway in NSW. The cemetery is mentioned in passing (heh).
The uneven terrain of Belmore Park perhaps provides us with the nearest idea of what the Devonshire Street Cemetery was like in its natural state as is possible today, although even it has a sordid and ugly past as an open gutter for the refuse of the nearby Belmore Produce Markets and Paddys Markets.
Rookwood Necropolis, Eastern Suburbs Memorial Park, Woronora Cemetery and many others were the recipients of many of the (not so) permanent residents of Devonshire Street, but none feature as striking and immediate a memorial as the tiny, eerie Camperdown Memorial Rest Park. Here, amongst the sombre atmosphere of tombstones and gloomy, gnarled trees lie what were once the gate posts met by visitors to Devonshire Street. These were removed along with everything else in 1901, and mysteriously disappeared from existence until 1946, when…
It seems almost sacrilegious that thousands of commuters tread all over this once-consecrated ground every day without any kind of marker to signify what was and who mattered, even if it was nearly 200 years ago. C’mon, NSW Government! They’re even in the right electorate! Meanwhile, to the 30,000 Sydneysiders scattered to the four corners by the winds of progress, the term ‘final resting place’ has little meaning.
Finally, here’s a fascinating account of a visit to Devonshire Street Cemetery just as its demolition was beginning. It originally appeared in the Clarence and Richmond Examiner, October 1 1901.