Bank of New South Wales/Westpac/Embassy Conference Centre – Chippendale, NSW
Oh, that’s nice.
But what’s this? Couldn’t make it through century two, then?
Actually, the Bank of NSW (later Westpac) held on here for a good 30 or so years past 1960. Let’s take a look:
As we’ve previously been over, the Bank of NSW has a long and illustrious hiszzz…huh, wha? Oh, do excuse me. The revered financial institution was established in 1817 without a safe. Yes, you read that right:
In the spirit of that ridiculousness, tomorrow I’ll be establishing an amusement park: Fast Rides of the Near Future. Anyone got any rides I can borrow? Free entry for a year if you do!
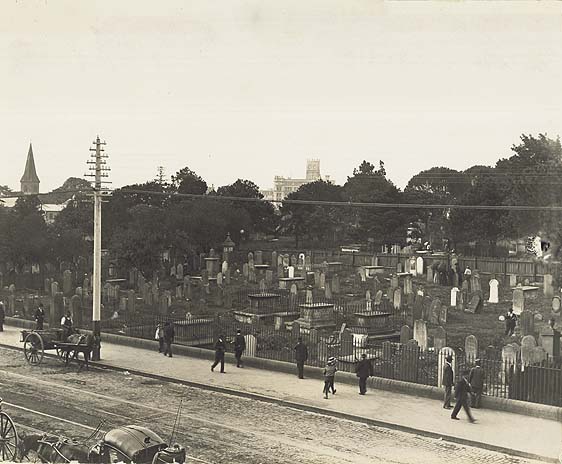
In 1860, the BoNSW started to branch out – literally. The bank’s first branch was established here on Broadway that year. But what flies in the ’60s sinks in the ’90s, and by 1894 changes had to be made. The powers that be summoned Varney Parkes (son of Sir Henry and former Bank of NSW employee) to design the current building (complete with it’s own gold smelting facility), unceremoniously treating their number one son like number two in the process. In fact (as we’ll see), that plaque at the top of the page is about as sentimental as Westpac cares to get (but remember, you’re not just a number 🙂 ).
Actually, maybe in 1955 you were. Oh, check it out: the postbox by the corner is still there!
1982 saw the Bank of NSW merge with the Commercial Bank of Australia to form Westpac, presumably to confuse customers. You can guarantee they would have netted some poor old biddy’s cash in the changeover. To aid the public through this confusing time, all branches were poorly rebranded with the Westpac name, and the Railway Square spot was no different.
Here it is in 1992, in glorious colour for the first time. In that same year, Westpac suffered a $1.6b loss, a record for any Australian corporation at the time. Staff were let go en masse, and that would had to have affected this branch. Luckily, anyone forced out the door would have seen the old Sydney City Mission logo behind them there. I wonder whatever happened to that? Someone should get on that.
Despite Westpac’s extensive refurbishment of the building in 1989-90, the bank was hit too hard by ’92’s recession. By 2000, the building that had once been the bank’s pride and joy was just another ‘For Lease’ along George Street, just in time for the Olympics.
Today, the bank’s purpose is to serve as a function centre. Why one would be needed right beside the Mercure, which presumably has its own, boggles the mind…unless. UNLESS…when the Mercure set themselves up, they put an ad in the paper advertising for the lend of a conference room…
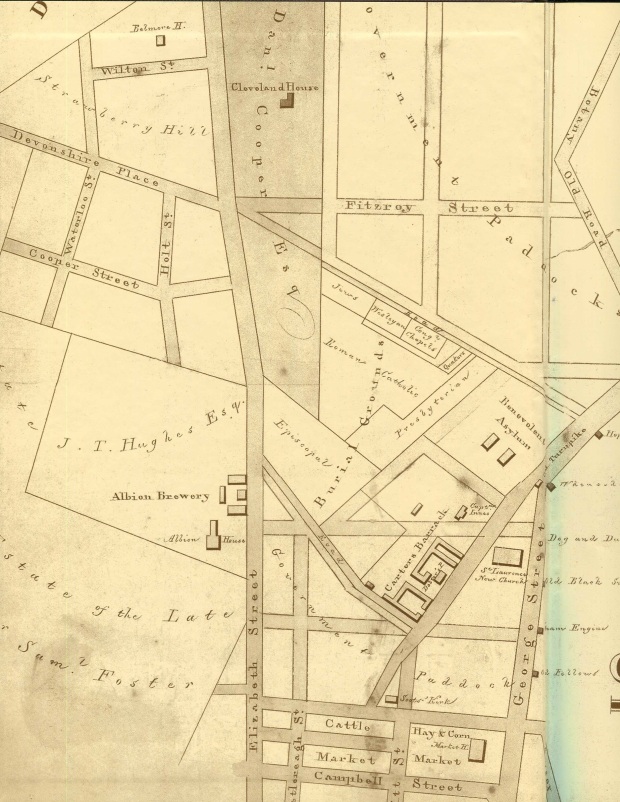
Devonshire Street Cemetery/Central Station – Sydney, NSW
“I once walked through the burial grounds on the Surry Hills, in the commencement of Spring, just as the flowers were beginning to bloom forth in all their beauty…”
Bridget Flood was in the same situation too many of us have found ourselves in all too often: stranded at Sydney’s Central train station, hopelessly late. The big difference is that she was waiting there for over 60 years.
As we’ve previously learned, 1820 was a good year to die in Sydney. Rather than ending up beneath the public piss-pot that was once the colony’s first burial ground, you could find yourself in a brand new plot freshly dug at the just-consecrated Devonshire Street Cemetery.
Chosen for its abundance of space and central (heh) location, the area bordered by Elizabeth and Devonshire streets was chosen to replace the Old Burial Ground as Sydney’s premier final resting place. Quartermaster Hugh McDonald, 40, was the first lucky stiff to be buried there following his death in 1819. Long waiting lists…so Sydney so chic.
“It was early in the morning when I commenced rambling amongst the tombs, the dew had not yet been dissipated by the genial rays of the invigorating luminary, and the cool fragrance of the atmosphere had not yet given way to the noon-day heat…”
Bridget Flood died in October 1836 at the age of 49 and, like virtually all deaths in Sydney at the time, was interred at the Devonshire Street site. Quoth her headstone:
“Pain was my potion
Physic was my food
Groans were my devotion
Drugs did me no good
Christ was my physician
Knew what way was best
To ease me of my pain
He took my soul to rest.”
They don’t write ’em like that anymore. And rest she did, as did all those buried at Devonshire Street Cemetery well past its 1867 closure.
Although steadily employed by the city’s dead between 1820 and 1866, the nail in the coffin (heh heh) for the cemetery was the latter year’s introduction of the Sydney Burial Grounds Act (NSW), which prohibited burials “within the city of Sydney from 1 January 1867, with the exception that persons with exclusive rights of burial at that date could still be buried on application to the Colonial Secretary who needed to be satisfied that ‘the exercise of such right will not be injurious to health’“. Phew. Just tie some rocks to me and throw me in the harbour!
You’d think this act would be in anticipation of some kind of grand plan for the burial ground, but no. With the exception of infrequent additions to family plots as outlined by the overly wordy act (and even these ceased in 1888), Devonshire Street was largely ignored by the growing city while new sites like Waverley Cemetery and the Rookwood Necropolis served the public’s burial needs.

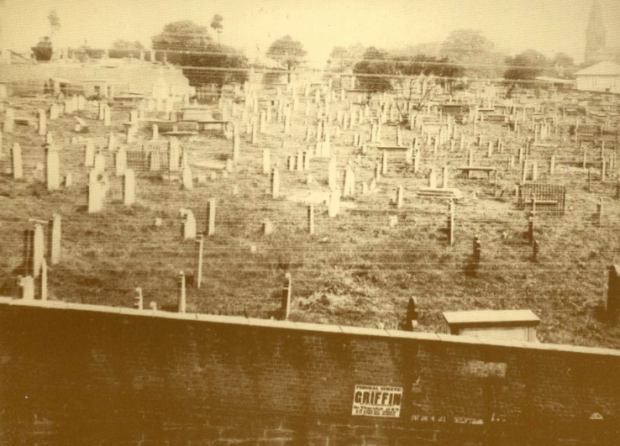
Prince Alfred Park’s Exhibition Building looms large. Devonshire Street Cemetery, 1901. Image courtesy Royal Australian Historical Society.
By 1900, its advanced state of neglect and decay reflected its residents and disturbed the public:
…although it wasn’t all bad:
“In short, it was exactly such an hour as an imaginative or sensitive being would delight to rove about, and lose himself in the regions of fancy…”
It wasn’t long before some of the more opportunistic voices began to speak out about the the site’s real estate value:
And as early as 1888 there were rumblings about how best to use the land:
It made sense, given that Central Station’s predecessor, ‘Sydney Station’, lay opposite the cemetery along Devonshire Street.
Since 1884, Sydney’s existing rail network had been under the stress of increasing traffic and a limited reach (sounds familiar, doesn’t it?). Sydney Station was constantly receiving upgrades and additional platforms, culminating in a messy setup of 13 train platforms and numerous tram sheds (sounds familiar, doesn’t it?). The city’s railway commissioners initially struggled to decide upon a plan for the future which would provide Sydney with a central hub expansive enough to extend the rail network to the suburbs (sounds- never mind).
An 1897 royal commission proposed the resumption of Hyde Park for use as the central terminal and, to counter the public outrage over the loss of parkland, the Devonshire Street Cemetery would be converted into a park. For a time this plan seemed to be a go until the unexpected death of Railway Commissioner E M G Eddy (of Eddy Avenue fame) that same year. This forced a literal return to the drawing board, where it was decided that it was probably easier to resume just one giant park instead of two. Nice thinking, guys.
In January 1901, the Department of Public Works served notice that anyone with relatives buried at Devonshire Street were to front up and make known their desire to have the remains reinterred at other cemeteries by train, with the cost to be borne by the NSW Government. These days, they’d just tell you to bring a shovel.
Unfortunately, these relatives were given a strict time limit of two months to act, and by the end of that time, only 8,460 bodies had been claimed (not among these was Eddy, who had been buried at Waverley following his death). This left 30,000 remains unclaimed, most of which were transferred to other cemeteries anyway, but due to the rushed nature of construction and given they did such a bang-up job the last time, it’s safe to say there are more than a few commuters at Central waiting for a train that will never come.
With that many bodies to exhume, you can imagine just how many creepy stories must have come out of the venture. Here’s just one:
The reason for the rush was that Melbourne had started work on their Central equivalent, Flinders Street Station, that same year. Sydney was determined to get the drop on Melbourne this time, as Flinders predecessor ‘Melbourne Terminus’ had been Australia’s first city railway station back in 1854, pipping Sydney by a year. The Devonshire Cemetery site had been completely cleared by 1902, and stage one of Central’s construction, which aimed to have the station operational, was completed in 1906. On opening day, the new station featured…13 platforms. Despite being twice the size of its predecessor, this was no improvement, and did nothing to alleviate Sydney’s transport woes (but then again, what ever does?).
“I directed my footsteps to a cluster of tombs on an eminence, which was thickly covered with green and blooming geraniums…”
But the unexpected fruit of the Department of Public Works’ labour was the emergence of commercial activity in the areas surrounding the new station. Its proximity to the city made department store shopping for those out in the sticks a treat, with Grace Bros., Marcus Clark, Anthony Hordern, Bon Marche and Mark Foy all within walking distance of Central by 1908. The Tivoli and Capitol theatres became entertainment meccas for those starved of entertainment in the ‘burbs.

Anthony Hordern awaits new business during Central’s construction, April 1903. Image courtesy ARHS Rail Resource Centre.
The station itself was hardly the thing of beauty its early designs had suggested, with the rushed development cycle omitting many intended features – least of all Central’s iconic clock tower, which wasn’t completed until 1924.
The construction wasn’t just focused on making sure the station would be operational before Flinders Street, though; there was particular care taken to ensure no trace of the Devonshire Street Cemetery remained, going so far as to completely eradicate Devonshire Street west of its intersection with Elizabeth. Other structures that once stood on the land now occupied by Central and its surrounds – the Belmore Police Barracks, the Benevolent Asylum, the womens refuge – have similarly been lost to time.
“I at first almost forgot the ravages of the grave in contemplating the enchanting appearance of the place.” – James Martin, 1838.
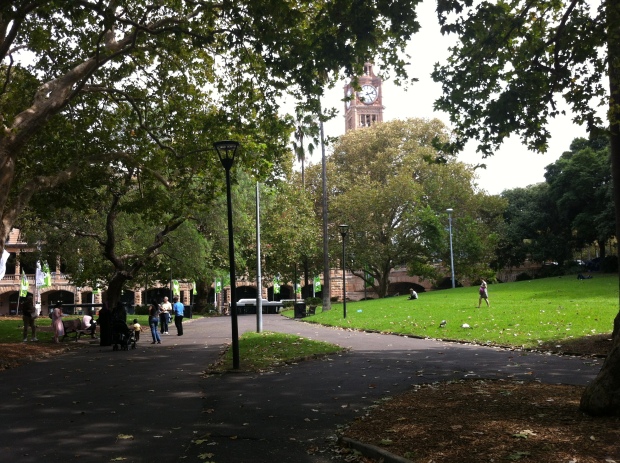
Today, nothing remains to remind commuters of the morbid nature of Central’s past. The cemetery itself was largely situated underneath today’s platforms:
Devonshire Street Tunnel, once Devonshire Street, runs directly underneath the path once carved between the cemetery and Sydney Station, depositing Surry Hills pedestrians into Railway Square amid el-cheapo bargain shops, youth hostels and fast food joints.
Also in Railway Square is a series of plaques designed to inform passers-by on the history of Central Station and railway in NSW. The cemetery is mentioned in passing (heh).
The uneven terrain of Belmore Park perhaps provides us with the nearest idea of what the Devonshire Street Cemetery was like in its natural state as is possible today, although even it has a sordid and ugly past as an open gutter for the refuse of the nearby Belmore Produce Markets and Paddys Markets.
Rookwood Necropolis, Eastern Suburbs Memorial Park, Woronora Cemetery and many others were the recipients of many of the (not so) permanent residents of Devonshire Street, but none feature as striking and immediate a memorial as the tiny, eerie Camperdown Memorial Rest Park. Here, amongst the sombre atmosphere of tombstones and gloomy, gnarled trees lie what were once the gate posts met by visitors to Devonshire Street. These were removed along with everything else in 1901, and mysteriously disappeared from existence until 1946, when…
It seems almost sacrilegious that thousands of commuters tread all over this once-consecrated ground every day without any kind of marker to signify what was and who mattered, even if it was nearly 200 years ago. C’mon, NSW Government! They’re even in the right electorate! Meanwhile, to the 30,000 Sydneysiders scattered to the four corners by the winds of progress, the term ‘final resting place’ has little meaning.
Finally, here’s a fascinating account of a visit to Devonshire Street Cemetery just as its demolition was beginning. It originally appeared in the Clarence and Richmond Examiner, October 1 1901.
John Storey Memorial Dispensary/Clinic 36 – Chippendale, NSW
Dwarfed by the apartment towers around Regent Street is this strange little corner building that looks almost medieval.
Closer inspection reveals that it was once the John Storey Memorial Dispensary, opened in 1926. Storey was a former NSW Premier who died in October 1921 after a lifelong battle with nephritis. No sooner was he in the ground than rumblings began about how best to honour his memory:
The paper alludes to the dispensary’s clientele as the city’s ‘sick poor’; what a diplomatic way of putting it. Today, the building is home to Clinic 36, and you’d be forgiven for thinking it might be a trendy bar. Nope, it’s a methadone clinic. Even after the deal was done to erect the Dispensary, the city officials weren’t satisfied that Storey’s name had been honoured enough:
I’m not exaggerating when I say that this letter goes on for a page and a half longer. They just didn’t care! Anyway, the point of the article is that a playground should be made to keep kids off the streets and out of crime’s way – a good cause, but as far as I can see the playground never materialised. But that’s okay, because even though it’s not quite as innocent as it was to begin with, Storey’s dispensary still looks after those children who’ve encountered the ‘evils of the street’.