Toyworld/Chuan’s Kitchen – Hurstville, NSW
When I turned four, I was taken for a walk up the street to the local toy shop and allowed to choose a present. The shop was a Toyworld – you remember, one of those big, purple deals with the giant purple bear wearing a cap in the modern fashion.
As a brand, Toyworld’s history dates back to 1976, when parent company Associated Retailers Limited realised that name wouldn’t look as good in rainbow colours on a toyshop marquee. Toyworld was launched as the retail group’s toy arm at a time when toys themselves were about to be ripped from their ancient comfort zones and thrust into a golden age of action figures by the blockbuster success of Star Wars. Riding this phenomenon from the late 70s through the mid 80s on brands such as Star Wars, Masters of the Universe and Transformers, Toyworld changed the face of toy retailers in Australasia, emblazoning that happy purple bear on hobby, sport and toy shops everywhere. Toyworld itself isn’t too sure about its own legacy, as the embarrassingly evident indecisiveness on its website demonstrates.

A man and his ride, 1981. Image courtesy whiteirisbmx/OzBMX.com.au
They didn’t entirely abandon their sporting goods heritage, either. Plenty of kids would have unwrapped a BMX (can you wrap a BMX? wouldn’t that look awkward as hell?) in front of jealous friends on birthdays or jealous siblings at Xmas, completely unaware that a purple bear had profited from their joy. For me, the sporting goods section of Toyworld was the absolute no-go zone. Who cared about some cricket pads when there were NINJA TURTLES over here? Or what about down there, in that bargain bucket out the front, for five bucks each?
On that glorious February day, I chose as my present the three Ghostbusters I was missing (I already had Venkman). My logic: I was turning four, and now I would have four of them. It worked – before long, the Ghostbusters were a team once more, zapping those crazy rubber ghosts until I saw an ad for Batman figures on TV and coloured Venkman black (see pic) in the hope he’d suffice. He didn’t.
And so my direct association with Alf Broome’s Toyworld ended, but I never forgot it. It was a hard place to forget purely on a visual level; from the purple frontage to the bear to the giant LEGO logo plastered on a mysterious door beside the shop, the whole place was designed to be an assault on a child’s senses, and oh what a glorious assault it was.
But what I didn’t know – couldn’t have known – at the time was the turmoil within. By 1988, Hurstville Toyworld was under siege, with struggles on local, national and even global fronts. Behind that happy purple face was a saga of bitterness and commercial impotence in the face a formidable threat to the entire toy industry.
As the article says, Broome’s toy shop had been around since 1971, first as the sports and toy shop, and then as Toyworld. Broome says that business boomed until 1986, when local opposition (likely the nearby Westfield, which had been constructed in 1978) made inroads into his business. The immediate effect of this encroachment was evident in the bargain bins outside – $5 Ghostbuster figures is a sign of the times.
Then, as Broome puts it, a “ripper recession” devastated any chance of recovery in 1990, with severe storm damage that same year not helping matters. Another strange point of impact upon sales mentioned by Broome was construction of a ‘new plaza’ by local council. Hmm…I’ll have to look into that one.
Broome banked it all on a healthy Christmas ’90 trading period that never came. The recently refurbished Westfield offered stiff competition, and globally, toys had begun their decline in popularity with the rise of video games. Even with the 1988 advent of the Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles, nothing could be done to stop the Nintendo/Sega tag-team, which by 1992 had all but ended the age of dedicated toy shops, relegating Barbies and He-Men to toy departments, or bigger chains like World 4 Kids. Rather than face the likelihood bankruptcy, Alf Broome chose to walk away.
That was 1991.
Today, the building still stands, despite the near constant construction and refurbishment of the area. Of course, it’s been standing there since 1899, and has probably seen more failure than you or I could ever imagine. The first post-Toyworld occupant was Belmontes Pizza Shop, and man was I ever bitter. I couldn’t believe the toy shop had gone, and pledged never to frequent the usurpers.
Chuan’s Kitchen, the current successor to a line of failed take-aways that has populated the site since Belmonte hit the bricks, was not open today even if I had wanted to spend cash there. The take-away might have enraged me, but what outright scandalised me as a child was that the mysterious door once adorned with that bright, colourful LEGO insignia had been replaced by an adult shop – as far from a kids toy shop as was commercially possible. Originally L.B. Williams’ Adult Book Exchange, today it’s the far more generic Hurstville Adult Shop.
Toyworld limps on, mostly in country locations. I swear, every country town I’ve ever visited has had a Toyworld. Why? And while I’m asking unanswerable questions: what was behind the door back when it had the LEGO sign on it? What did Alf Broome do next? Just who was L.B. Williams? Perhaps we’ll never know. But Alf, if you’ve Googled yourself and have ended up here, I want you to know something. Back in 1991 you may have been “the man in the wrong place, at the wrong time, in the wrong business”, but in 1989, when I went in and was gifted those Ghostbusters, your shop was the world to me. And this is just my story – imagine the number of kids who would have left that purple shop happier than they’d ever been. Heck, reader, it might have been YOU. That kind of thing might not have been able to pay rent, staff wages or stock prices, but it does guarantee your immortality, Alf. You’re welcome.
ARCHAEOLOGICAL UPDATE:
It’s cool when things like this happen. As you’ve read above, I presented my case on the flimsiest bit of evidence, but Your Honour, I now present to the court…EXHIBIT B.
When the building behind it was demolished, it allowed for a prime view of the back of Chuan’s Kitchen. Why should this matter? Let’s take a closer look…
Oh, what’s that? I can’t quite make it out…CLOSER STILL!
Boom. There it is. Today. You could go and see it right now. At some point in the Toyworld saga, they thought to put up this logo on the reverse side of their building. Why?
Perhaps at the time the Liquor Legends building wasn’t there, providing uninterrupted views of the beaming purple signage. Maybe the signwriters were doing a two-for-one deal and the owner was going to get his money’s worth, damn dammit. Or maybe the truth is far more sinister… Either way, it took the demolition of the bottle shop (all in the name of progress) to unearth this treasure. Within each seed, there is the promise of a flower. And within each death, no matter how big or small, there is always a new life. A new beginning.
Police Citizens Boys Club/Police Citizens Youth Club – Burwood, NSW
 According to the Police Citizens Youth Club website, the organisation is “about young people”, but it wasn’t always that way. This year, the PCYC is celebrating its 75th anniversary of “getting young people active”, “developing young leaders”, and “protecting young people”, but if you were a girl back in 1938, you could pretty much get bent as far as the cops were concerned.
According to the Police Citizens Youth Club website, the organisation is “about young people”, but it wasn’t always that way. This year, the PCYC is celebrating its 75th anniversary of “getting young people active”, “developing young leaders”, and “protecting young people”, but if you were a girl back in 1938, you could pretty much get bent as far as the cops were concerned.
 According to the side of the Burwood branch, it’s about boys. Who knows, in another 75 years, it may even include old people.
According to the side of the Burwood branch, it’s about boys. Who knows, in another 75 years, it may even include old people.
Pizza Hut/Salvation Army – Liverpool, NSW
If there’s one goal that’s proven consistently hard to achieve, it’s covering up an eat-in Pizza Hut. There seem to be two typical approaches: the first is to make a genuine effort to alter the building and hope no one recognises. It doesn’t always work. The second is to just embrace the hallmarks of the former tenant wholeheartedly, and who better to breathe new life into someone’s sloppy seconds than the Salvos?
Inside, if you can look past the piles of instructional golf videos and copious amounts of Fifty Shades of Grey, it isn’t hard to spot the former Hut infrastructure that hasn’t already been sold off. Heck, someone probably walked away with the original oven for a bargain price, and I’m kicking myself right now that it wasn’t me.
Even the toilets have been put to a more hygienic use (but not by much) as change rooms. And no, I would not count among the highlights of my blogging career standing in the middle of a Salvation Army and taking a photo of its change rooms. It’s all for you, Damien.
When my generation returns to the earth and Pizza Hut’s eat-in legacy is forgotten, will people wonder why these buildings look so odd? Probably not.
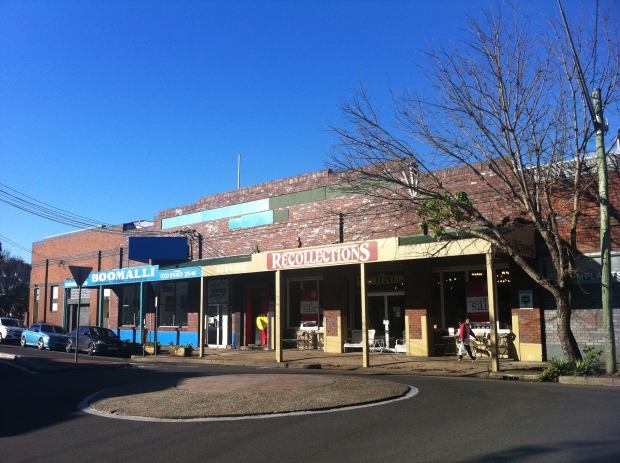
Della Cane/Boomalli & Recollections – Leichhardt, NSW
These days, Leichhardt is home to Recollections, a country-style furniture warehouse, and one door up is Boomalli, an Aboriginal artist cooperative. In this instance, Recollections have wisely chosen to drop their full business name so as not to create a microcosm of colonial Australia right here on Flood Street.
But the earliest settler at this warehouse lives on through this tiny little detail. It’s old, it’s worn, it’s even got a bit snapped off…but it’s still just strange enough to make an observant passer-by take pause. Leichhardt’s hardly a tropical paradise. What’s the story?
The answer lies back in 1991, and this ad for Della Cane. No building that ugly could exist twice, and the interior looks like Fantastic Furniture met Jurassic Park.
Past/Lives Flashback #1: Union Carbide – Rhodes, NSW
Original article: Timbrol Chemicals/Union Carbide/Residential – Rhodes, NSW
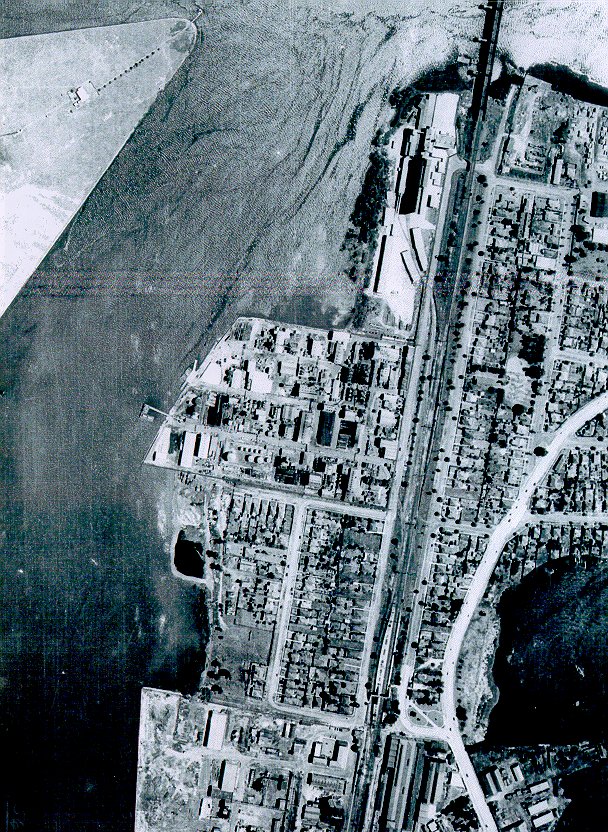
Yes, the time has finally come. The most popular entry on Past/Lives over the last year (and a bit, by this point) by far was the tragic tale of Rhodes and that most toxic tenant, Union Carbide. Rhodes’ decimation at the hands of industrial abuse throughout the 20th century and subsequent resurrection as a residential paradise in the 21st is a long story, and one with repercussions for the whole of Sydney even today. Grab a coffee (although Rhodes residents, maybe don’t use tap water) and get comfortable…we’ll be going back over the whole thing.
THEN
Rhodes Hall, near Leeds, was about as far from the eastern shore of the picturesque Homebush Bay as Thomas Walker could imagine. A commissary, Walker had arrived at Port Jackson in 1818, and the following year bought an allotment of land from Frederick Meredith, another early settler. Walker built a house on his bank of the Parramatta River, naming it Rhodes after his grandmother’s estate back in the motherland because even hardened and worldly mercenaries still have soft spots for their grannies. So soft, in fact, that in 1832, Walker moved to Tasmania where he built another estate…also named Rhodes. She must have spoiled that kid rotten.
The Walker family relinquished their control over the Rhodes estate in 1919, when they sold up to the John Darling Flour Mill. By this point, Rhodes was no stranger to industry. Eight years earlier, G & C Hoskins had cleared much of the area’s forests to erect a cast iron foundry, and once this had happened, everyone got on board. There was little resistance to this kind of heavy industrialisation, especially in a suburb like Rhodes, which was easily accessible by rail and water.

Kind of looks like the silhouette of a guy with a ponytail, doesn’t it? Image courtesy City of Canada Bay.
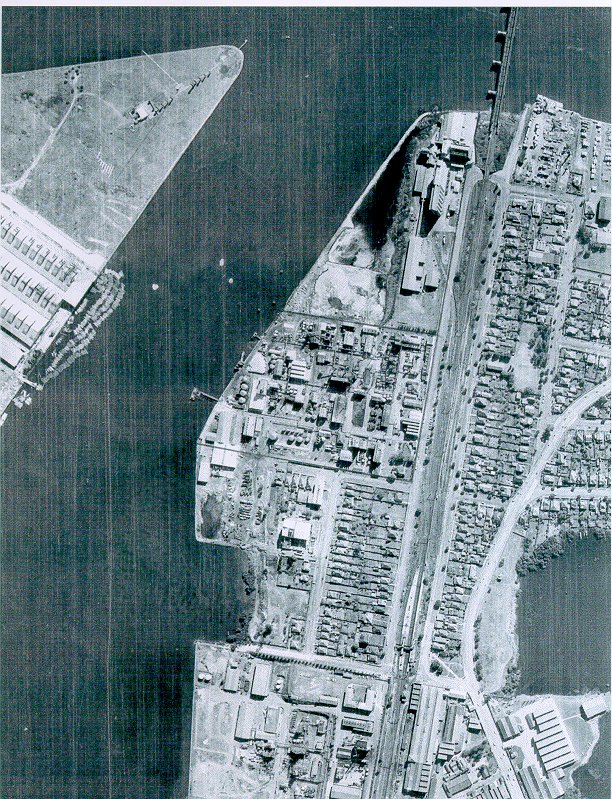
At this point in time, Rhodes and the neighbouring Homebush were the outer limits, truly the Western Suburbs, with only Parramatta and the Blue Mountains more forbidding. Sydneysiders were keen to get the blossoming industrial sector as far away from their own backyards as possible (understandably), and Rhodes, bordered by the new abattoir and the Parramatta River, was out of sight, out of mind.
Flour mills and cast iron foundries weren’t exactly environmentally friendly (a phrase not yet in use in 1928), but the true damage to Rhodes didn’t begin until the arrival of Timbrol Ltd in 1928. Timbrol had been established in 1925 by three Sydney University researchers keen to manufacture their own brand of timber preservative, so at least it was all for a good cause.
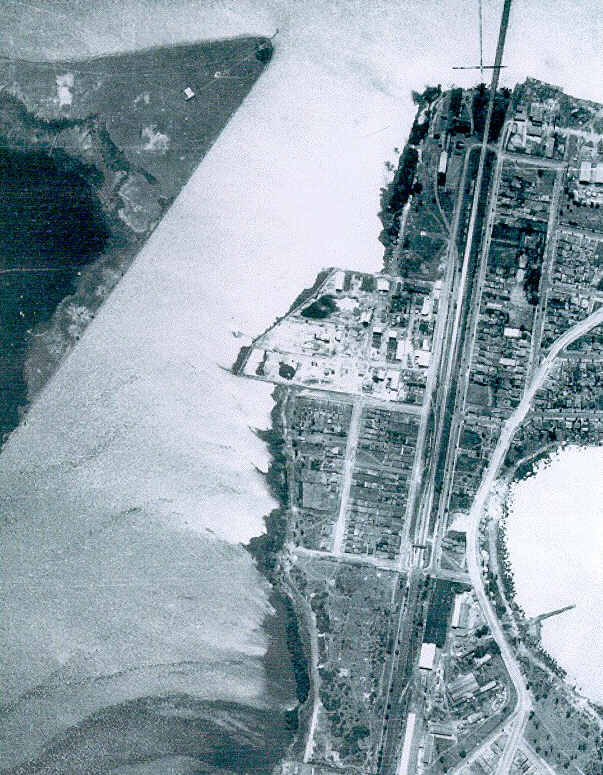
In 1933, Timbrol had a breakthrough! It was able to produce the first Australian made xanthates, which is used in the mining sector for extracting particular kinds of ores. With the advent of the Second World War, xanthate exports boomed, and expansion of the Timbrol site was required. But where to go? Sandwiched between the train line and the foreshore, and with John Darling to the north and CSR (another booming wartime chemical company) to the south, Timbrol was apparently out of options.
Just joking. Of course there was an option – the only option: reclaim land from Homebush Bay by filling in the river with contaminated by-products and building over it. Out of sight, out of mind.
The post-war housing boom brought about various new challenges in the domestic domain, most of which could be easily solved with chemicals. Thus, demand for chlorine, herbicides and insecticides, particularly DDT, skyrocketed, and Timbrol was right there to capitalise. And by right there, I mean jutting out over Homebush Bay on new, hastily constructed ground.
Spurring the chemical company’s efforts on even further were their competitors CSR, ICI and Monsanto, most of whom were a stone’s throw away from the Timbrol site. The close proximity of these companies meant that the output of potentially dangerous by-product seemed minimised in the eyes of the era’s governments; it was better for all the companies to be dumping together rather than dumping apart at wider intervals. This also meant that the neighbouring sites could ‘borrow’ Timbrol’s approach to expansion – good news for Homebush Bay.
Timbrol’s success had attracted another element: the American chemical giant Union Carbide, which saw Timbrol as a great place to start an Australian subsidiary. Union Carbide dated back to 1898, and had built its wealth through aluminium production and its zinc chloride battery arm – both of which seem like the perfect thing to manufacture on the bank of a serene body of water.
At this point I’d like to pose a question: when did it ever seem like a good idea to produce chemicals like herbicides, zinc chloride and xanthates beside a healthy bay full of wildlife? Who signed off on this? How were the guys in charge of these companies able to look at this beautiful place and think “Hmm, needs more poison.”? I’m aware that without these chemicals we wouldn’t be able to live the way we do today, but some of these decisions were bordering on just straight up evil.
The arrival of Union Carbide frightened Timbrol’s competitors. The might of the American parent company meant near-unlimited resources, so local campaigns were stepped up.
CSR and even old John Darling began to encroach upon the bay, re-sculpting the landscape as they saw fit.
The initial success of Union Carbide Australia didn’t go unnoticed overseas, either. Associated British Foods bought John Darling’s Flour Mill for its Australian subsidiary Allied Mills in 1960, rebranding it Allied Feeds. Most of the product manufactured at the Allied Feeds site would end up in the stomachs of livestock sent to Homebush Abattoir, where said stomachs would then be carved up to be fed back to the populace. And for that, you need MORE ROOM.
But back to Union Carbide. The early 1960s weren’t kind to UC. Competitors and waning demand had teamed up to diminish the brand, but that didn’t stop the near endless flow of poisons into the bay. By now, nearly all of Union Carbide’s output produced an unfortunate and extremely unpleasant by-product: dioxins. Highly toxic and capable of, at the very least, causing cancer and damaging reproductive and immune systems, dioxins are usually exposed to humans via food particularly meat and fish. What a great idea then to produce extremely unsafe levels of dioxins right beside a manufacturer of animal feed. What a great idea to produce that animal feed on top of land infused with dioxins. What a great idea to expel those unwanted dioxins into Homebush Bay, a waterway directly linked to Sydney Harbour and full of fish.
Let’s take a moment to hear from the World Health Organisation about dioxins:
Short-term exposure of humans to high levels of dioxins may result in skin lesions, such as chloracne and patchy darkening of the skin, and altered liver function. Long-term exposure is linked to impairment of the immune system, the developing nervous system, the endocrine system and reproductive functions. Chronic exposure of animals to dioxins has resulted in several types of cancer. Due to the omnipresence of dioxins, all people have background exposure and a certain level of dioxins in the body, leading to the so-called body burden. Current normal background exposure is not expected to affect human health on average. However, due to the high toxic potential of this class of compounds, efforts need to be undertaken to reduce current background exposure.
So…don’t do what Union Carbide did next, then?
The fortunes of Union Carbide Australia were reversed by the Vietnam War. See, Vietnam has a lot of jungles, and those pesky Vietcong kept hiding in those jungles, so what better way to flush them out than by removing their hiding spot? Union Carbide was contracted by the US military to produce Agent Orange, a dioxide-heavy defoliant. Even when it was discovered that Agent Orange’s components contained a particularly toxic strain of dioxin, it continued to be sprayed indiscriminately throughout the war, during which dioxins continued to be dumped into Homebush Bay.
In the midst of all this, Union Carbide research scientist Douglas Lyons Ford invented Glad Wrap at the Rhodes plant. It was introduced to the Australian market in 1966, the first such product in the country. Well, that kind of balances out that other thing, doesn’t it?
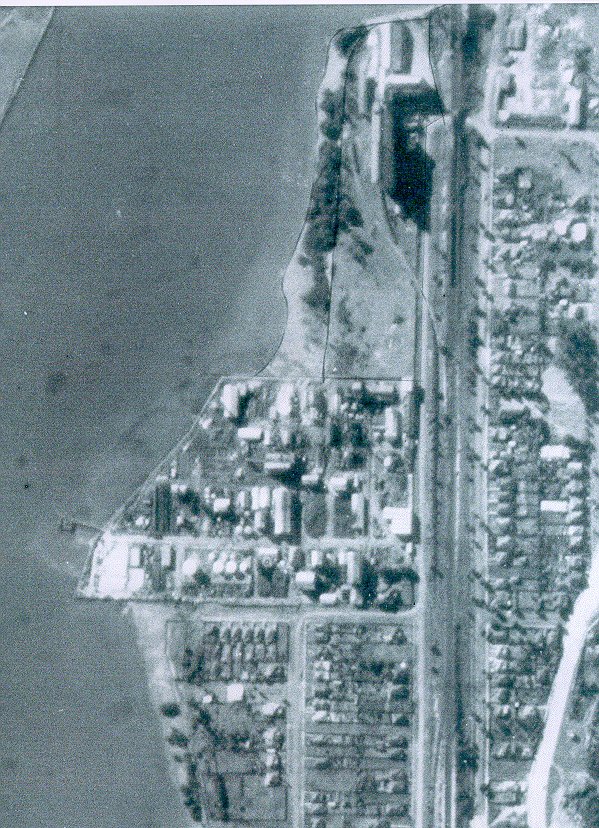
By the 70s, environmental action against companies like these was stepping up, and the population of Sydney had exploded westward. Rhodes’ train line was now a sharp divider between the industrial zone and a booming residential sector.
Further north and across the river, Meadowbank and Ryde were both beginning to cast aside their industrial legacies and welcoming more and more families, while to the south, the Homebush Abattoir was winding down operations. Forward-thinking residential developers were eyeing these areas with great interest, and keeping government wheels greased to ensure their availability in the future. In typical lightning fast Sydney reaction time, this movement was accommodated in the mid-80s by the construction of Homebush Bay Drive, a highway that bypassed the nearby suburb of Concord and tracked through Rhodes’ industrial zone. Out of sight, out of mind.
By the early 1980s, Rhodes was known throughout the land for its toxicity and odour above all else.
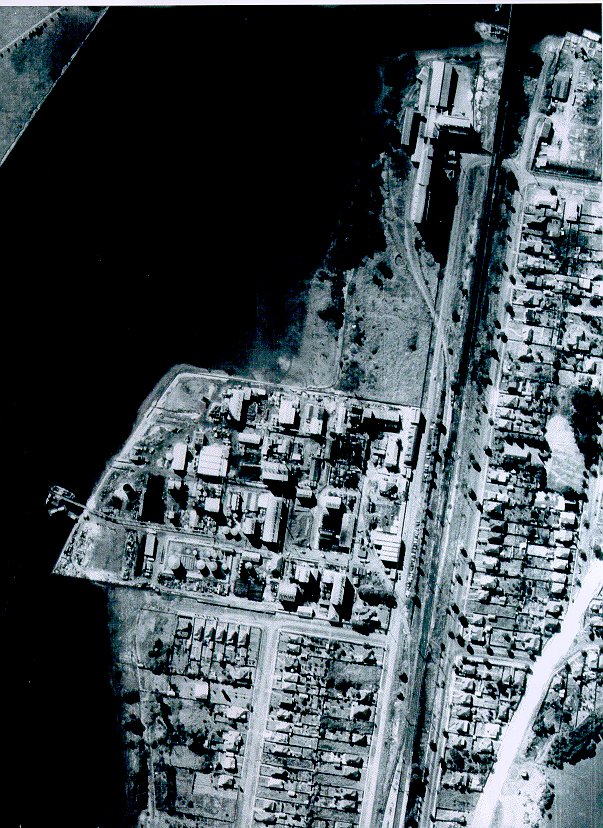
Its rich legacy of achievements in the field of chemistry long forgotten, Union Carbide was looking increasingly sick and tired; a relic of another age. But one major incident in 1984 made it look downright villainous.
In December of that year, an explosion at the Union Carbide plant in Bhopal, India exposed half a million people to toxic gases, killing thousands. PR disaster for UC, and the final straw for the parent company. Most of its international subsidiaries were wound up in the years following Bhopal, including the Rhodes plant, which ceased operations in 1985. Allowed to leave without any kind of cleanup effort, Union Carbide left behind a toxic legacy that remains detrimental to Sydney today.
The NSW Government and the Australian Olympic Committee had hoped to transform Rhodes into an Olympic athlete village by the 2000 Sydney games, but they had underestimated just how poisoned the land was.
Government remediation efforts tried in vain between 1988 and 1993 to heal the land, but it wasn’t until 2005, long after the end of the Olympics, that private enterprise intervene with the necessary money and technology to properly clean the land. Why this sudden burst of effective effort so long after the fact?
NOW
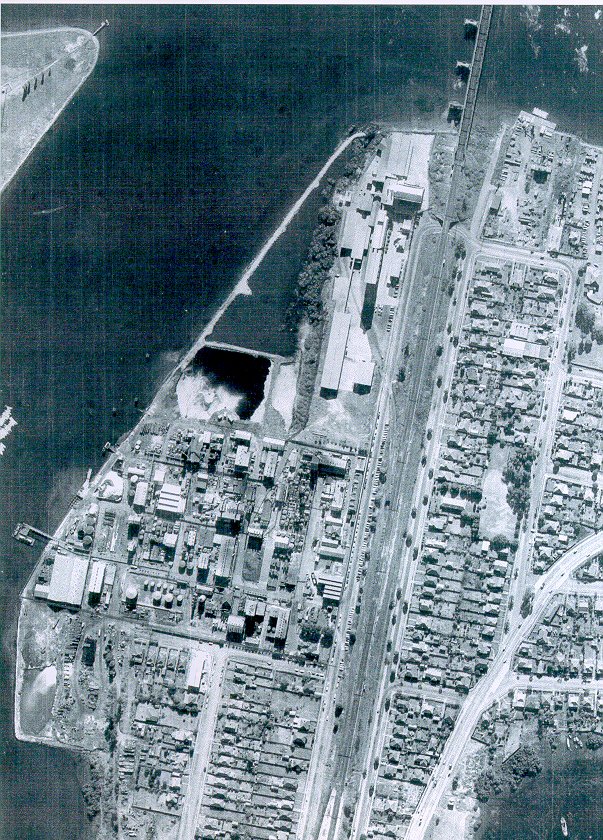
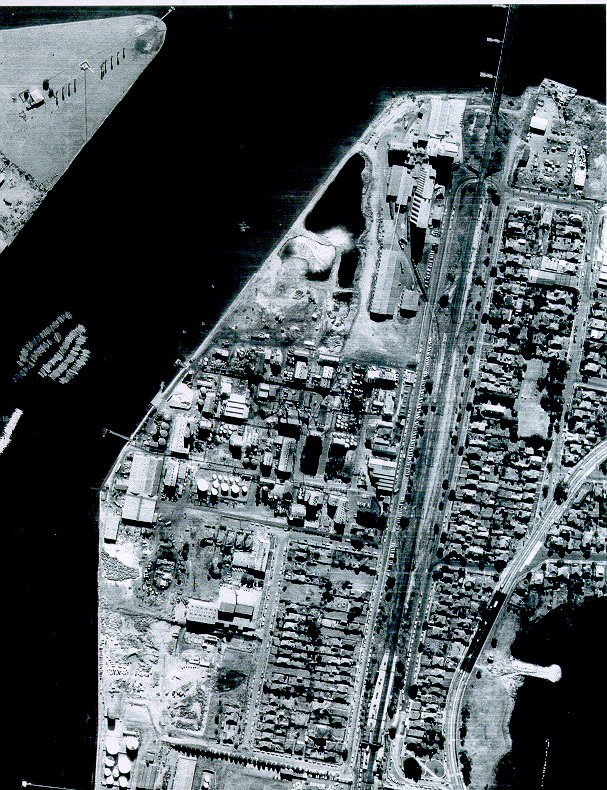
Today, if you turn off Homebush Bay Drive at the IKEA, you’ll descend into valleys of glass and steel. Rhodes’ rebirth as a gauntlet of residential and commercial towers, a process which began in 2005, is nearly complete. Sensing an opportunity to make money, Mirvac and other developers pounced on the toxic wasteland at the end of the 90s, saving it from a future of causing people to hold their breath as they drove past.
With a steady flow of money and the promise of even more at the end of the remediation rainbow, Thiess and the NSW Government got to work turning the poisonous dirt into the foundations of the futuristic castles that line the foreshore today.
But while the reclaimed land has been mostly made harmless, the bay has not. In fact, the NSW Department of Health has prohibited fishing west of Sydney Harbour Bridge due to an abundance of dioxins. And swimming? Forget it.
The remediation efforts have been effective in more ways than one. I don’t think that Mirvac and friends really cared about anything other than making the land safe enough to pass re-zoning as residential, but despite this, wetland wildlife has begun to return to the bay. Studies on the sea life are ongoing with hopes that one day the bay will once again be safe, but I don’t think we’ll see it in our lifetime. To my infant readers: this means you too.
To the developers’ credit, the project seems to have largely been a great success. There’s the popular shopping centre, complete with cinema and IKEA (a huge coup in its day, since superseded by Tempe), and Liberty Grove to the east. Care has been taken to eradicate most traces of the industrial nightmare of the past. The new units look good enough to stop you from wondering why the grass is always yellow, and they’re certainly filling up fast. And yet…
If you plant a seed in bad soil, it won’t grow very well. Case in point: this is the unit tower being constructed directly upon the former Union Carbide site. Every other tower in Rhodes is either completed or is only weeks away, but not Union Carbide. In fact, the entire site seems to have been plagued with construction delays or other issues. Sure, this stage of the Rhodes project started later than the others, but that too is down to the sheer toxicity of the Union Carbide land.
At the rear, things look even worse. Piles of dirt sit around, uglifying the scenery. Cranes hover above the unfinished structure like buzzards.
On the corner of Shoreline and Timbrol, construction equipment is a mainstay. It’s as if they just can’t make this one happen, despite their money and intentions.
Tower number two hasn’t even started yet, acting as a base of operations for the workers completing tower number one. In 1997, Greenpeace discovered 36 sealed drums of toxic waste underneath the Union Carbide site, so there’s no telling what these guys are digging up as they go. Does your underground carpark glow in the dark?
Down at the Union Carbide foreshore, an even eerier sight: completed units, completely empty.
These seem to be ready to go, but either due to environmental concerns or the noise of construction, residents aren’t allowed to move in yet. I’d be leaning toward the former reason, seeing as plenty of other people here have to put up with the noise.
The Rhodes experiment has proven to be an environmental triumph, arguably even greater than Sydney Olympic Park, but it’s an even greater financial triumph. The corporations behind the remediation weren’t doing this for the sake of the environment or because they felt like doing something nice, they were doing it for the exact same reason the land was stained in the first place. Rhodes may have gotten the second chance Bhopal never did, but they’re equally valid testaments to that reason.